Understanding Landed Costs in Odoo
Landed cost in Odoo helps businesses allocate additional costs (such as freight, customs duties, insurance, and handling fees) to purchased products. These costs ensure accurate product valuation, especially for inventory-managed items.
When applying landed costs in Odoo, the cost can be distributed using different split methods based on business needs. Let's explore them in detail with practical business cases.
A. Split Methods in Odoo Landed Cost
Odoo provides the following methods to distribute landed costs:
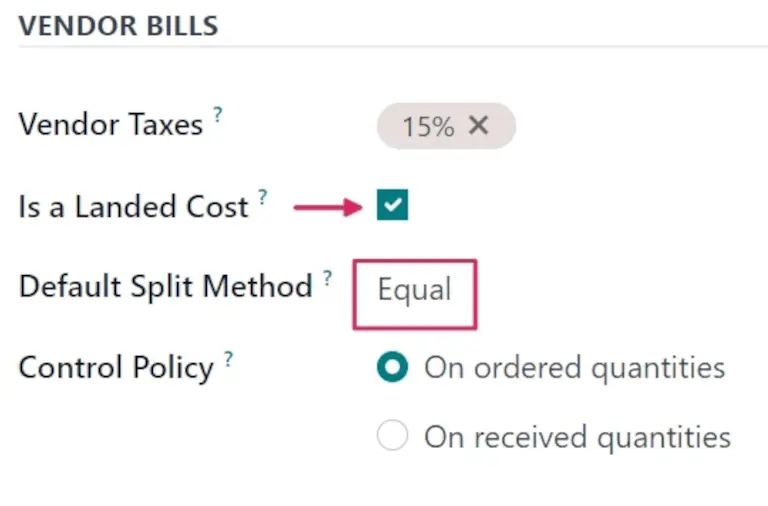
- Equal (Manual Distribution)
- By Quantity
- By Current Cost (Value-Based)
- By Weight
- By Volume
B. Explanation with Business Cases
2.1. Equal (Manual Distribution)
👉 Explanation: The additional cost is evenly divided among all selected products, regardless of their quantity, weight, or value.
✅ Best for: When all products should bear an equal share of the cost.
📌 Business Case:
A company imports 3 different electronic components for a trading unit. The freight cost of Rs 100 is to be allocated. Since all components share the shipping equally, the cost is divided equally across all products.
Product | Quantity | Landed Cost (Freight)
Freight Charges Product1 10.00 ₹ 116.67 ₹ 150.00 ₹ 33.33
Freight Charges Product2 20.00 ₹ 233.33 ₹ 266.66 ₹ 33.33
Freight Charges Product3 30.00 ₹ 350.00 ₹ 383.34 ₹ 33.34
2.2. By Quantity
👉 Explanation: The landed cost is distributed proportionally based on the number of units received.
✅ Best for: When additional costs depend on the number of units.
📌 Business Case:
A furniture company imports chairs and tables, and the freight cost is Rs 120. Since all items take up the same shipping space per unit, cost allocation is based on quantity.
Product | Quantity | Landed Cost Per Unit
Product 1 10 pcs Rs 10 ₹ 100.00 ₹ 116.67 ₹ 16.67
Product 2 20 pcs Rs 10 ₹ 200.00 ₹ 233.33 ₹ 33.33
Product 3 30 pcs Rs 10 ₹ 300.00 ₹ 350.00 ₹ 50.00
2.3. By Current Cost (Value-Based)
👉 Explanation: The cost is distributed based on the existing cost of the products.
✅ Best for: When landed costs (like insurance or customs duty) depend on product value.
📌 Business Case:
A jewellery business imports gold rings and diamond necklaces. Since insurance and customs fees are based on value, the costs are allocated proportionally.
Product Current Cost % of Total Value Landed Cost (Freight Rs 120)
Freight Charges Product1 10.00 ₹ 100.00 ₹ 115.19 ₹ 15.19
Freight Charges Product2 12.00 ₹ 240.00 ₹ 276.46 ₹ 36.46
Freight Charges Product3 15.00 ₹ 450.00 ₹ 518.35 ₹ 68.35
2.4. By Weight
👉 Explanation: The landed cost is distributed based on the weight of the items.
✅ Best for: When freight charges are dependent on weight.
📌 Business Case:
A steel manufacturing company imports steel sheets and rods. The shipping fee is $300, and weight-based distribution is the best fit.
Product Weight (kg) % of Total Weight Landed Cost
Freight Charges Product1 10.00 ₹ 100.00 ₹ 108.57 ₹ 8.57
Freight Charges Product2 20.00 ₹ 240.00 ₹ 274.29 ₹ 34.29
Freight Charges Product3 30.00 ₹ 450.00 ₹ 527.14 ₹ 77.14
2.5. By Volume
👉 Explanation: The cost is distributed based on the volume occupied by the product.
✅ Best for: When shipping costs depend on space occupied (e.g., air freight, cargo).
📌 Business Case:
An automotive company imports car bumpers and dashboards, and the shipping cost is $1,000, mainly influenced by how much space each item takes.
Product Volume (m³) % of Total Volume Landed Cost
Freight Charges Product1 10.00 ₹ 100.00 ₹ 111.76 ₹ 11.76
Freight Charges Product2 20.00 ₹ 240.00 ₹ 277.65 ₹ 37.65
Freight Charges Product3 30.00 ₹ 450.00 ₹ 520.59 ₹ 70.59
C. Choosing the Right Split Method
Business Need VS Best Split Method
Equal distribution - Equal
Large quantity items should get a lower cost - By Quantity
Expensive items should get more cost - By Current Cost
Heavy items should get more cost - By Weight
Large-sized items should get more cost - By Volume
4. Conclusion
Landed cost allocation in Odoo is determined by business needs and cost drivers. By selecting the appropriate split method, companies can accurately reflect the actual cost of their products, resulting in more accurate pricing and profitability analysis.